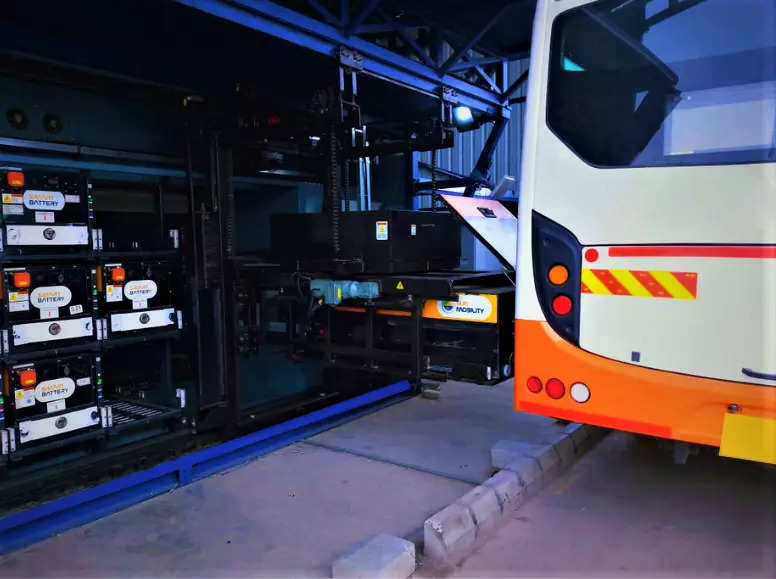
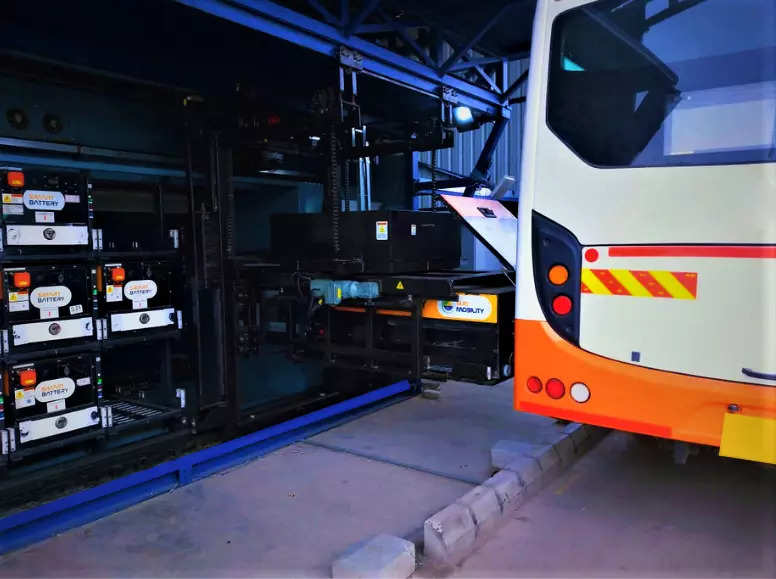
India is likely to soon fix standards for swappable batteries for electric buses to bring ease in battery change at any accessible station, a senior government official said.
The latest standards, which will deal with size, weight and capacity, seek to bring about interoperability of batteries meant for e-buses. “There is a need for more coordinated technology deployment in e-buses,” the official told ET, adding that interoperability of e-buses is a key focus now.
At present, e-bus makers use proprietary batteries that are customised to fit into the vehicles and vary in capacity and weight with negligible interoperability.
Only charging of batteries has been standardised in government tenders. “Having common battery swapping stations for all the e-buses in a city is the way ahead for reducing infrastructure requirements and improving output,” the official said. “Highways should also have swapping stations which can serve all e-buses.”
These standards are likely to be firmed up soon, he said, adding that the proposed norms will help address range anxiety in e-bus operators who do not want to face battery discharge mid journey.

Interoperability will pave the way for batteries that can be quickly changed at the nearest swapping stations on highways, or bus depots in urban areas, the official said.
The Ministry of Heavy Industries had earlier asked battery swapping stations and two-wheeler manufacturers to thrash out a consensus over interoperability. But the ministry has now decided to formulate norms after they failed to agree. In the present model, e-buses are procured by central agencies and then handed over to state transport utilities (STUs) who operate the buses and recover costs. The STUs are responsible for paying back the bus makers.
There has been a preference for plug-in charging for e-buses in the procurement tenders.
To catalyse adoption, the Centre in August 2023 launched the PM e-Bus Sewa Scheme, aiming to deploy 10,000 buses. While the plug-in technology is established, time required for charging from 0-100% is about 6-8 hours for slow charging and 2-3 hours for fast charging.
Also, larger capacity batteries cause a reduction in passenger carrying capacity and increase the vehicle weight.
Experts said the government and the industry should work towards making batteries more efficient but said the shift towards e-buses should be calibrated. “The battery swapped e-bus should operate more like a CNG vehicle which does not need as much refuelling time,” said Shivanand Swamy, emeritus director of the Centre of Excellence in Urban Transport at CEPT University, Ahmedabad.